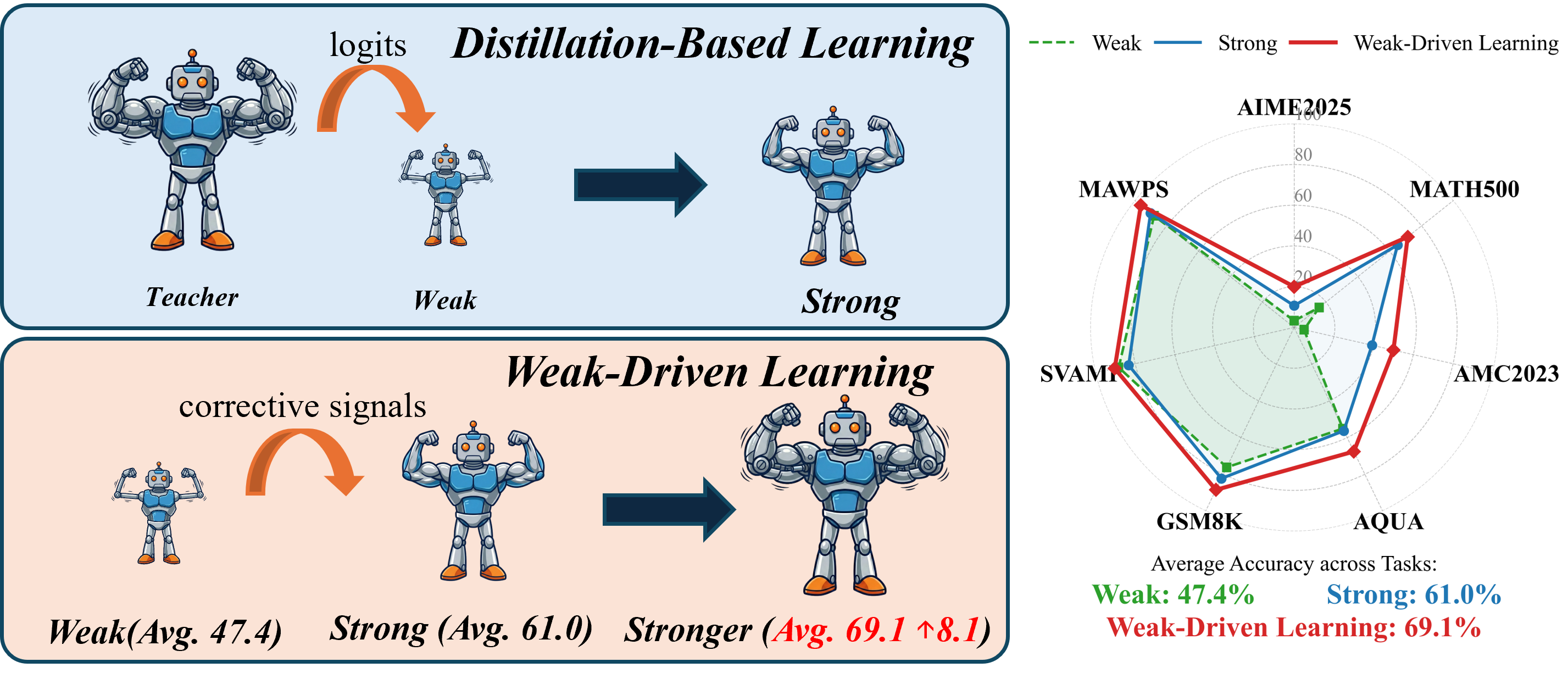
Weak-Driven Learning
Highlights
Weak-Driven Learning introduces a novel post-training paradigm that challenges the conventional assumption that learning with weaker models necessarily degrades performance. Key features include:
- Novel Learning Paradigm: Leverages weak agents (historical model checkpoints) as informative error signals to drive continuous improvement beyond standard supervision saturation.
- No Additional Inference Cost: The enhanced model maintains the same architecture as the base model, requiring no extra computational overhead during inference.
- Consistent Performance Gains: Demonstrates improvements on challenging benchmarks including mathematical reasoning and code generation tasks, compared to standard SFT baselines.
- Practical Training Framework: Implements joint optimization of weak and strong models through logit mixing, preventing gradient vanishing and maintaining effective learning pressure.
Model Overview
This repository contains models trained using the Weak-Driven Learning framework, which operationalizes the principle that weak agents can make strong agents stronger (WMSS). Unlike knowledge distillation that requires access to stronger teachers, weak-driven learning leverages easily obtainable weak reference models such as historical checkpoints.
Key Contributions
- Learning Paradigm: Introduces a post-training approach that highlights the overlooked role of weak agents as driving signals for improving strong agents.
- Training Framework: Proposes joint optimization through logit mixing that compels the strong model to refine its decision boundary and sustain meaningful gradients in saturated regimes.
- Theoretical Foundation: Provides gradient-level analysis demonstrating how incorporating weak-model logits reshapes the optimization landscape and prevents gradient vanishing.
- Empirical Validation: Shows consistent improvements on mathematical reasoning and code generation benchmarks.
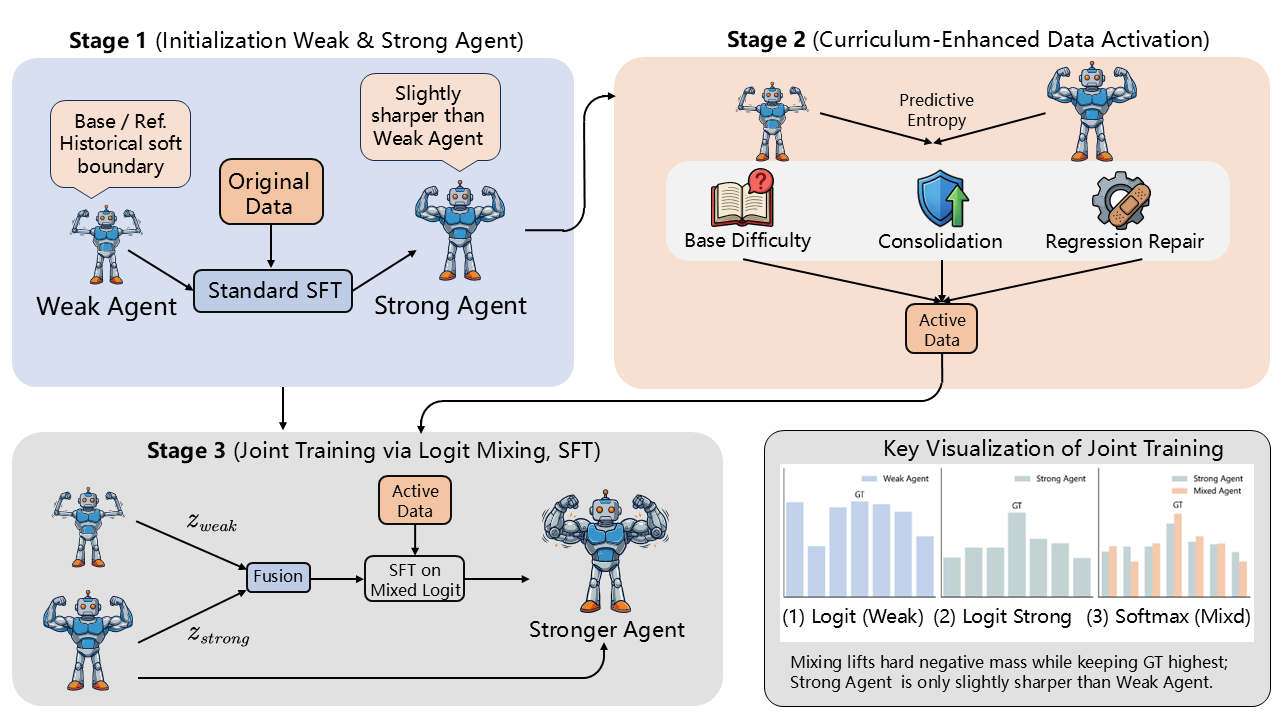
Training Methodology
The framework consists of three phases:
Phase 1: Initialization
- Prepare the base model and compute initial entropy on training data
- The base model serves as the "weak agent" in subsequent training
Phase 2: Curriculum Learning with Entropy-Weighted Sampling
- Train the first-stage model using entropy-based weighted sampling (BrownBoost-style)
- Focus on challenging samples where entropy differences are significant
- This model becomes the "strong agent" for joint training
Phase 3: Joint Training
- Jointly train weak and strong models through logit mixing
- The mechanism prevents gradient vanishing on non-target tokens
- Extract the enhanced sub-model with improved capabilities
- No additional inference cost: Extracted model has the same architecture as base model
Model Specifications
This model is trained using the Weak-Driven Learning framework with the following specifications:
- Base Model: Qwen3-4B-Base
- Type: Causal Language Model
- Number of Parameters: 4.0B total (3.6B non-embedding)
- Architecture: Qwen3 (Transformer-based)
- Number of Layers: 36
- Attention Heads: 32 for Q, 8 for KV (Grouped Query Attention)
- Context Length: 32,768 tokens (training with max sequence length 8,192)
- Training Data: AM-1.4M dataset (AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled, filtered and processed)
- Training Hardware: 8× NVIDIA H800 GPUs
- Training Framework: TRL + Hugging Face Transformers + DeepSpeed
Training Hyperparameters:
- Learning rate: 1×10⁻⁵
- Maximum sequence length: 8,192
- Weak-Driven Learning parameters: α=0.1, β=0.8, γ=0.1
- Logit mixing coefficient: λ=0.5
Key Dependencies:
transformers>=4.57.1trl>=0.25.1torch>=2.8.0vllm>=0.11.0(for inference)
Model Variants
We provide models trained with Weak-Driven Learning on different base models:
| Model | Base Model | Parameters | Context Length | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak-Driven-Learning-4B | Qwen3-4B-Base | 4.0B | 32K | Mathematical reasoning, code generation, resource-constrained environments |
| Weak-Driven-Learning-8B | Qwen3-8B-Base | 8.0B | 32K | Complex reasoning tasks, advanced code generation |
All models are trained using the same three-phase Weak-Driven Learning framework with identical hyperparameters.
Hardware Requirements
Inference
| Model Size | Minimum VRAM | Recommended VRAM | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4B | 8GB | 16GB | FP16/BF16 |
| 8B | 16GB | 24GB | FP16/BF16 |
For longer context lengths (>8K tokens), additional memory may be required.
Training
- Recommended: 8× NVIDIA H800 (80GB) or A100 (80GB) GPUs
- Minimum: 4× NVIDIA A100 (40GB) GPUs with gradient accumulation
- DeepSpeed ZeRO-3 optimization recommended for memory efficiency
Quickstart
Installation
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/chenzehao82/Weak-Driven-Learning.git
cd Weak-Driven-Learning
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
Inference Example
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "chhao/Weak-Driven-Learning"
# Load the tokenizer and model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
# Prepare the model input
prompt = "Solve the following math problem: If x + 2 = 5, what is x?"
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# Generate response
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=2048,
temperature=1.0,
top_p=0.95,
top_k=40
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
response = tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print("Response:", response)
Deployment
Using vLLM
vLLM provides high-throughput and memory-efficient inference for LLMs.
# Install vLLM
pip install 'vllm>=0.11.0'
# Launch OpenAI-compatible API server
vllm serve chhao/Weak-Driven-Learning --port 8000 --tensor-parallel-size 2
Using the API
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
base_url='http://localhost:8000/v1',
api_key="EMPTY"
)
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': 'Solve: 2x + 3 = 11'}]
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
messages=messages,
model="chhao/Weak-Driven-Learning",
max_tokens=2048,
temperature=1.0,
top_p=0.95
)
print(completion.choices[0].message.content)
Training Your Own Model
To train your own model using the Weak-Driven Learning framework:
1. Prepare Training Data
cd dataprocess
python am_deepseek_r1_distilled.py
This generates:
am_deepseek_r1_filtered_ad.jsonl— main training dataam_deepseek_r1_filtered_ad_test_1000.jsonl— test subset
2. Configure Training Parameters
Edit scripts/run_ensemble.sh:
GPU_USE: GPU device IDsbase_model: Base model path (e.g.,Qwen/Qwen3-4B-BaseorQwen/Qwen3-8B-Base)outdir: Output directory for checkpoints- Training hyperparameters (learning rate: 1×10⁻⁵, max sequence length: 8,192, etc.)
- Weak-Driven Learning parameters (α, β, γ, λ)
3. Run the Complete Pipeline
cd Weak-Driven-Learning
bash scripts/run_ensemble.sh
The script automatically executes the three-phase training pipeline:
- Initialize base model and compute initial entropy
- Train first-stage model with curriculum learning
- Jointly train weak and strong models, then extract the enhanced sub-model
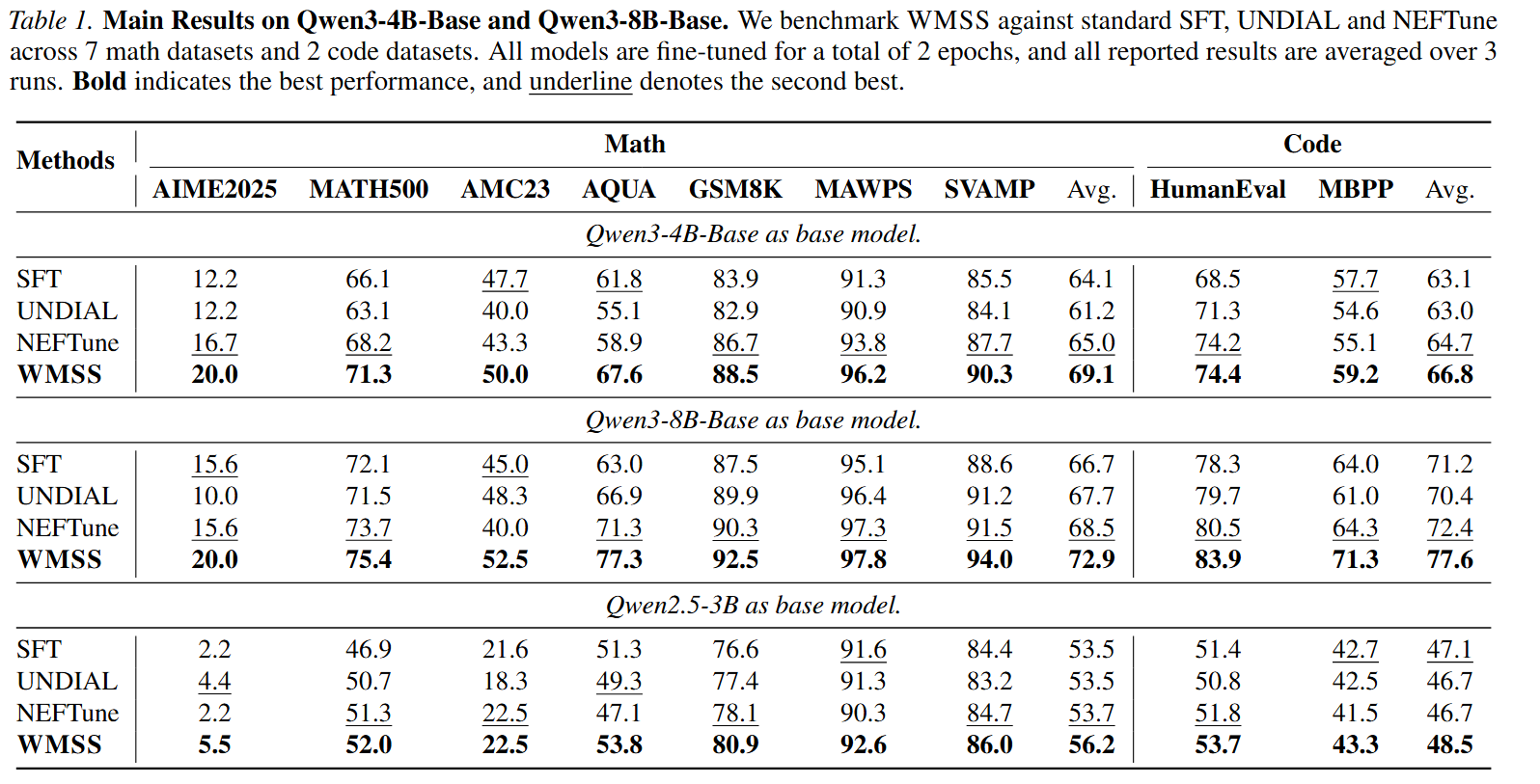
Evaluation Results
Our method consistently improves performance on challenging benchmarks compared to standard SFT baselines. These gains arise purely from improved optimization dynamics during training and incur no additional inference cost.
Best Practices
Inference Parameters
For optimal performance, we recommend the following sampling parameters:
temperature=1.0top_p=0.95top_k=40
Task-Specific Recommendations
Mathematical Reasoning:
- Use the model's chat template for structured input
- Allow sufficient
max_new_tokens(2048-4096) for detailed reasoning chains - The model benefits from step-by-step problem decomposition
Code Generation:
- Provide clear problem specifications and constraints
- Use appropriate context length for complex codebases
- The model can handle multi-file code generation tasks
Limitations
While Weak-Driven Learning demonstrates consistent improvements, users should be aware of:
- Training Data Dependency: Performance is influenced by the quality and diversity of the AM-1.4M training dataset
- Domain Specificity: The model is optimized for mathematical reasoning and code generation; performance on other tasks may vary
- Computational Requirements: Training requires significant GPU resources (8× H800 GPUs recommended)
- Base Model Constraints: Inherits limitations from the base Qwen3 model architecture
Project Structure
Weak-Driven-Learning/
├── scripts/ # Training pipeline scripts
│ └── run_ensemble.sh # Complete three-phase training pipeline
├── ensemble/ # Core training and evaluation
│ ├── ensemble_train.py # Joint training implementation
│ ├── run_entropy.py # Entropy computation
│ ├── extract_submodel.py # Extract enhanced sub-model
│ └── eval_vllm_thinking_math.py # Evaluation script
├── utils/ # Model fusion, entropy, and data processing
│ ├── fuse_models.py # Logit mixing and model fusion (WMSS)
│ ├── compute_entropy.py # Entropy computation algorithms
│ └── weight_datasets.py # Entropy-based weighted sampling
├── EnsembleQwen3/ # Qwen3 ensemble model definitions
│ ├── configuration_qwen3.py # Model configuration
│ └── modeling_qwen3.py # Model architecture with logit mixing
└── dataprocess/ # Data processing scripts
Citation
If you find our work helpful, please cite our paper:
@misc{chen2026weakdrivenlearningweakagents,
title={Weak-Driven Learning: How Weak Agents make Strong Agents Stronger},
author={Zehao Chen and Gongxun Li and Tianxiang Ai and Yifei Li and Zixuan Huang and Wang Zhou and Fuzhen Zhuang and Xianglong Liu and Jianxin Li and Deqing Wang and Yikun Ban},
year={2026},
eprint={2602.08222},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2602.08222}
}
Links
- Paper: arXiv:2602.08222
- Hugging Face Paper Page: Weak-Driven Learning
- GitHub Repository: Weak-Driven-Learning
- Model Weights: chhao/Weak-Driven-Learning
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What makes Weak-Driven Learning different from knowledge distillation?
A: Unlike knowledge distillation that requires a stronger teacher model, Weak-Driven Learning uses weaker models (like historical checkpoints) as reference points. By explicitly identifying and distancing from weak model failure modes, the strong model continues to improve beyond standard supervision saturation.
Q: Does the model have additional inference overhead?
A: No. After training, we extract the enhanced sub-model which has the same architecture as the base model. There is zero additional inference cost compared to standard fine-tuned models.
Q: Can I use this framework with other base models?
A: Yes! The Weak-Driven Learning framework is model-agnostic. While we provide implementations for Qwen3, the methodology can be adapted to other transformer-based architectures. See the GitHub repository for implementation details.
Q: What is the AM-1.4M dataset?
A: AM-1.4M is a high-quality dataset derived from AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled, containing 1.4 million samples focused on mathematical reasoning and problem-solving. The dataset is filtered and processed to ensure quality and diversity.
Acknowledgments
- Model architecture based on Qwen models
- Training framework built on TRL and Hugging Face Transformers
- Training data derived from AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled dataset
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
- Downloads last month
- 12